QR Code Phishing, also known as “Quishing,” is a sophisticated cyber threat that leverages the ubiquity of QR (Quick Response) codes to orchestrate phishing attacks. QR Code phishing can be thwarted with the help of an advanced AI email security pioneer, Trustifi, which tracks all attacks on its clients with its security operations (SecOps) teams. The SecOps team witnessed a 250% increase in hacks that obliterated QR codes from July to September in 2023.
Scammers can exploit QR codes via numerous platforms, including emails, SMS, social networks, public areas, or even by personally persuading people to scan them.
The FBI has noted a surge in deceptive individuals guiding victims to use physical cryptocurrency ATMs and QR codes for payment transactions.
These swindlers frequently trick victims into executing payments and direct them to withdraw money from their financial holdings, such as investment or retirement funds.
The FBI warns that the victim will be provided with a QR code connected to the scammer’s digital currency wallet for the transaction.
The swindler will subsequently lead the victim to a physical cryptocurrency ATM, where they can deposit their money, purchase digital currency, and use the provided QR code to automatically input the recipient’s address.
Here’s an insight into its modus operandi:
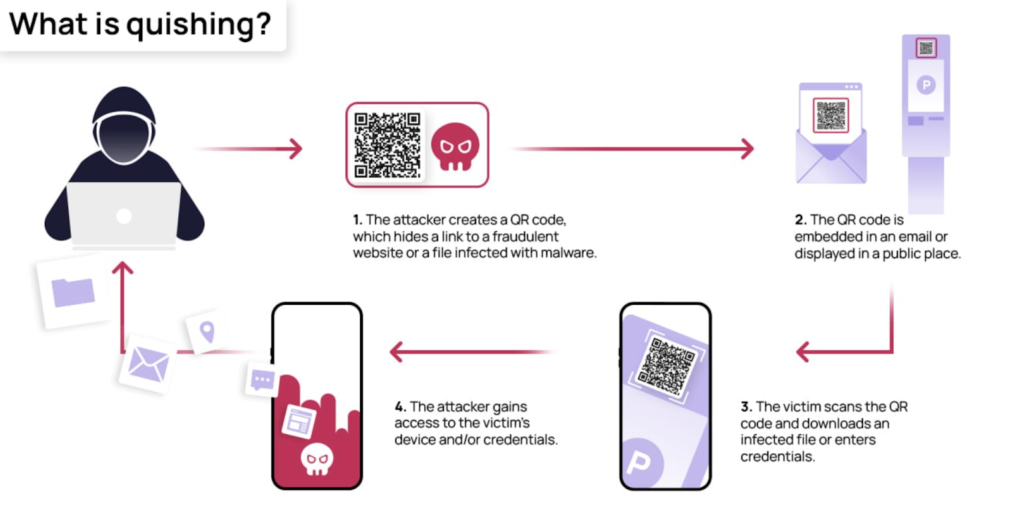
Crafting a Malicious QR Code: Cyber adversaries engineer QR codes that, upon scanning, redirect users to fraudulent websites or trigger the download of malicious software. These QR codes can be disseminated via various mediums, including emails, social media, print materials, or even by superimposing them over authentic QR codes in public spaces.
The Deception Mechanism: The moment an individual scans the QR code, they are navigated to a counterfeit website that might bear a striking resemblance to a legitimate one. Here, they are coaxed into divulging sensitive information such as login credentials, personal data, or financial details. Certain QR Code Phishing attempts may also lead to the download of malware, compromising devices and networks.
Exploiting QR Code Popularity: QR Code Phishing capitalizes on the recent surge in the usage and growing popularity of QR codes. These codes, easily scannable using smartphones, are perceived as harmless and have become an indispensable tool for businesses and organizations to share information, streamline payments, or direct users to websites. This trust and familiarity are exploited in QR Code Phishing attacks.
FBI Reports on Scammers: The FBI has noted a rise in scammers directing victims to use physical crypto ATMs and QR codes for payment transactions. Scammers often deceive victims into making payments and instruct them to withdraw funds from their financial accounts, including investment or retirement accounts. The FBI warns that a QR code connected to the scammer’s cryptocurrency wallet will be provided to the victim for the transaction.
Preventing QR Code Phishing: QR Code phishing can be thwarted using cutting-edge AI email security. The SecOps team observed a 250% increase in hacks that overwrite QR codes from July to September in 2023.
Shielding Yourself from QR Code Phishing Attacks
In the digital age, QR code phishing, or ‘quishing’, has emerged as a significant threat. Here are some strategies to fortify your defenses against such attacks:
1. Authenticating QR Code Origins: Before scanning a QR code, it’s crucial to authenticate its source. It’s advisable to scan QR codes only from trusted sources, like official websites or branded products and services. Exercise caution with unsolicited QR codes.
2. Choosing a Trustworthy QR Code Scanner: Opt for a QR code reader developed by a reputable software company. Some of these applications come equipped with security features.
3. Previewing the Destination URL: Certain QR code readers offer the functionality to preview the destination URL before you’re redirected to it. This can help you steer clear of malicious websites.
4. Exercising Caution in Public Spaces: Be vigilant about QR codes in public spaces. Fraudsters often overlay their malicious QR codes over legitimate ones.
5. Avoid Scanning QR Codes from Strangers: If you receive a QR code from an unidentified sender, it’s safer to avoid scanning it.
6. Regular Software Updates: Keeping your software updated can shield you from known security vulnerabilities.
7. Employing Advanced Anti-Phishing Tools: Consider the use of sophisticated anti-phishing tools. These can offer protection from a broad spectrum of phishing attacks, including those leveraging QR codes.
Always remember, if you have doubts about a QR code, it’s safer to refrain from scanning it.
Trustifi: An AI Email Security Pioneer in the Fight Against QR Code Phishing
Trustifi, a leader in AI Email Security, has broadened its OCR scanning capabilities to encompass QR codes integrated with its highly praised Inbound Shield module. Trustifi’s OCR scanning feature meticulously inspects the QR code object, hunting for any concealed URLs and other potentially damaging content that has already been scrutinized by Trustifi’s AI filtering engines.
Conventional email security solutions that lack the integration of machine learning and AI protective layers offer limited advantages to organizations in terms of phishing.
Trustifi, along with other AI-powered email security solutions, incorporates several AI-protection filters that examine embedded URLs and thwart impersonation attacks from initiating post the initial email phishing attempt.
Trustifi’s AI-powered email security leverages its vast data sets within its Large Language Model (LLM) to produce intricate behavior analytics for identifying malicious content in QR code attacks and AI-generated text messaging.
The prevention of advanced AI-driven attacks is a primary focus of Trustifi’s email security expertise. The company’s innovative application of AI and machine learning distinguishes it, leading to enhanced email protection efficiency and streamlined incident response.
Trustifi’s Email Detection and Response (EMDR)
Trustifi’s sophisticated AI-powered inbound shield scans every attachment, searching for key indicators of a QR Code Phishing attack:
- Does the QR Code URL code contain HTTP or HTTPS prompting the user for a username and password?
- Is the QR code URL domain legitimate or misspelled?
- Is the QR Code redirecting the user to a known phishing site?
- Is the QR code attempting to download malicious malware after the user presses the image?
Trustifi’s robust AI-filtering engine identifies these malicious attack methods, preventing these QR codes from launching attacks against their client’s devices. Trustifi’s AI engines evolve as more of these types of QR codes transform into new attack vectors. This learning process is the cornerstone of Trustifi’s ongoing success in thwarting AI-enabled hacker attacks.
Trustifi OCR Scanning
Trustifi’s most recent feature includes a machine-learning OCR scan that automatically encrypts critical email files. Trustifi, a SaaS email security company, has today incorporated an AI-powered functionality into its industry-leading email encryption and DLP product that utilizes OCR.
Even when attack vectors evolve, Trustifi’s ability to monitor all incoming emails for domain impersonation, rogue URL links, and plain text messaging that persuades users into clicking on QR codes is unparalleled.
Trustifi’s award-winning Inbound Shield module now scans QR codes using QCR scanning.
OCR scanning inspects QR codes for embedded URLs and other rogue material previously filtered by Trustifi AI. OCR scanning is seldom included in legacy email security systems, including secure email gateways.
Risk of QR Code Phishing
The theft of personal and confidential data is a significant risk.
Financial Deception: There’s a danger of direct financial theft or fraud, especially when sharing payment details.
Malware Threat: Certain deceptive tactics can lead to the download of harmful software, jeopardizing the security of devices and networks.
Trust Dilemma: The escalating issue of QR Code Phishing has led to a distrust in QR codes, which can drastically reduce their utility for legitimate uses.
Be wary of divulging your login details, as this can result in unauthorized access to your personal or work accounts.
Organizational Hazards Potential Security Breaches: If an employee falls victim to a phishing attack, unauthorized individuals may gain access to the company’s networks and sensitive information.
Reputation Harm: If an organization gets entangled in a phishing attack, either as a target or due to compromised systems, it could severely tarnish its reputation.
Financial Losses: In addition to direct theft, companies may suffer financial losses due to the need for remediation, increased cybersecurity measures, and possible legal implications.
Addressing Cybersecurity Issues Distribution of Malware: QR Code Phishing is a technique that can be used to distribute harmful software, compromising devices and networks.
The extensive use of QR codes has considerably amplified the opportunity for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities, posing a greater challenge in maintaining robust security measures.
Targeting Vulnerable Populations: Less tech-savvy Individuals may be more susceptible to phishing attempts, putting them at a higher risk of being targeted.
Societal Impact Decline in Trust of QR Codes: Regular QR Code Phishing attacks can undermine people’s trust in QR codes, making them less effective and less likely to be adopted.
Frequent exposure to such strategies may cause users to become desensitized to suspicious activity, making them more susceptible to other forms of cyberattacks.
Potential Legal Consequences for Organizations: Companies that fail to adequately protect their data may face legal repercussions, particularly under data protection regulations like GDPR.
Compliance Challenges: Organizations must ensure their cybersecurity policies and practices are current to effectively counter evolving threats, which can demand substantial resources.
Naorem Mohen is the Editor of Signpost News. Explore his views and opinion on X: @laimacha.


AI can significantly reduce QR code phishing risks by verifying codes before they’re scanned. Using a reliable, free QR code generator ensures the codes are secure, reducing the chances of malicious redirects. Stay safe by choosing trusted tools!
https://qrcodechamp.com/